How Does a Gold IRA Work?
How often do you think about your retirement savings and investments? Do you feel like you’ve adequately diversified your portfolio? Have you considered gold as a potential vehicle for your future financial security?
If you’ve stopped to think about these questions, there’s a good chance you’ve considered investing in gold or other precious metals. But you may not know the details on how to invest in gold as part of your retirement account (IRA).
Traditionally, an IRA is a plan that holds paper investments like stocks, bonds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and treasury notes. How is a Gold IRA different? You can still own all the paper assets you want to own. But, inside your plan, you can also hold physical gold bars and coins, stored and tucked away for safekeeping.
Yep, you heard that right—real, physical gold inside your IRA.
Although it may sound complicated, it isn’t. We’ll break it all down for you right here, and you’ll understand how to invest in a Gold IRA in no time.
What Is a Gold IRA?
A Gold IRA (sometimes called a precious metals IRA or self-directed IRA) uses physical gold or other precious metals like silver, platinum, or palladium bullion. This differs from traditional IRAs, which usually include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. Some people use gold IRAs to diversify their retirement savings. Others invest in gold as a hedge against inflation and for additional stability in their portfolio.
Types Of Gold IRA
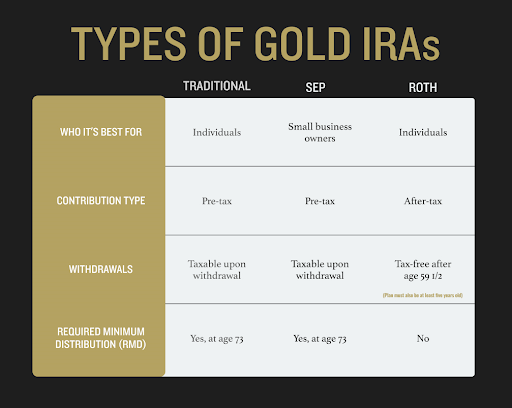
There are three types of Gold IRA:
- Traditional
- Simplified employee pension (SEP)
- Roth
Each type has its own rules and can meet the various needs of different investors and their circumstances.
Traditional
If you currently have an employer-sponsored, tax-deferred retirement plan, such as a 401(k), but wish to sock away more money on a tax-deferred basis, or if you have left a job and still have a 401(k) sitting there, then a traditional IRA may be for you. The traditional IRA is a favorite of those who look to their future and expect to be in the same or a lower tax bracket during retirement.
Traditional IRAs have contribution limits set by the IRS that you must adhere to. However, depending on your situation, the contribution to your traditional IRA may be fully tax deductible. Withdrawals from the plan may begin, without penalty, at age 59½, and you must begin required minimum distributions (RMDs) at age 73. Much like the SEP IRA, withdrawals are taxed as regular income.
Your certified public accountant (CPA) or tax advisor can clarify your specific contribution limits and level of deductibility.
SEP
If you are self-employed or own a business and don’t have access to an employer-based retirement plan, a simplified employee pension IRA is for you. The SEP, funded by you, allows you to look toward the future.
Because it may be your only source of retirement planning, SEP plans allow the owner to put away much more money than the typical individual retirement account. For 2023, the SEP allows up to $66,000 or 25% of compensation, whichever is less. SEP contributions are typically tax-deductible in the year they are made, but they are taxed at the time of withdrawal.
Unpenalized withdrawals can begin at age 59½, and RMDs must begin at age 73.
Contact your tax advisor or CPA to determine if a SEP is right for you.
Roth
A Roth Gold IRA is for those who expect their future earnings to be greater than they are now and will likely be in a higher tax bracket later in life.
You contribute to a Roth Gold IRA with after-tax funds—meaning you pay the taxes upfront. Because you’ve already satisfied the tax obligation on the initial contribution, the investments in a Roth grow tax-free. You will not have any taxable consequence when, following IRS guidelines, you take distributions or withdraw funds from the plan.
To withdraw without penalty or taxation, you must be 59½ years old, and the plan must have been in place for five years. You won’t pay taxes as your investments grow, and you may take tax-free withdrawals during your retirement.
Unlike traditional plans, Roth IRAs never require you to take mandatory withdrawals, and when handed down to heirs, their withdrawals are also tax-free.
Roth plans do have income limits for eligibility, so not everyone will qualify for this type of plan. Be sure to check with your tax advisor.
What Is A Custodian?
A custodian is a bank or financial institution that manages your retirement account.
Think of a custodian as your personal IRA valet. They facilitate your account’s required paperwork, reporting, and regulatory compliance. The custodian also ensures funds flow smoothly from one account to another and informs you of any consequence or obligation arising from said transfers.
Your statements will come from your custodian, who can answer questions regarding account balances, distribution requirements, and other concerns.
How To Fund A Gold IRA
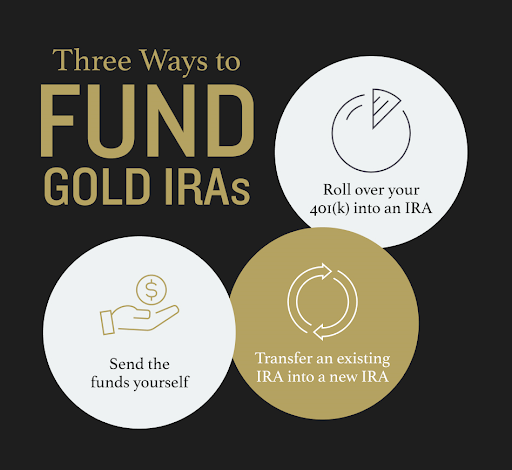
After you have consulted your CPA or tax advisor to decide what type of IRA is right for you, and you understand the eligible contribution limits for your situation, you can fund your Gold IRA in one (or a combination) of three ways:
- Direct contribution
- IRA transfer
- 401(k) rollover
Direct Contribution
With a direct contribution, you have funds available and earmarked for investment, and you send those funds to the IRA custodian via check, wire, or traditional mail. The custodian deposits them into your account and makes the funds available for investing.
IRA Transfer
IRA transfer occurs when you already own an existing IRA and instruct your current custodian to move your assets directly into a different IRA, whether at the same firm or with a different one. The direct transfer stays tax and penalty-free, as the funds remain in an IRA.
401(k) Rollover
You can use a 401(k) rollover to fund an IRA directly, meaning funds route straight into your new or existing IRA from your 401(k) account. There is typically no tax consequence or penalty for this rollover, as funds move from one institution to another, and no distributions are taken.
An indirect 401(k) rollover varies in that the funds are sent from the 401(k) to the account holder, and the account holder then has 60 days to deposit them wholly into another eligible account, such as a Gold IRA. Assuming that the entire amount is deposited within the allotted period, no penalty is assessed, and there is no tax consequence.
Types Of IRA-Approved Precious Metals
Whether you have your eye on shiny coins or your heart set on gleaming bars of gold, plenty of approved metals are eligible for your Gold IRA.
The IRS has strict guidelines for IRA-eligible gold and other metals.
Gold must be at least 99.5% pure, except for the Gold American Eagle coin. The Eagle is the USA’s flagship 1-ounce coin and contains 1 pure ounce of gold, but it actually weighs slightly more than an ounce and therefore misses the 99.5% purity standard. Of course, it is allowed!
The guidelines also stipulate that:
- Coins must be minted by approved government mints, be new, uncirculated, and in perfect physical condition.
- Proof coins must come with certificates of authenticity.
- Eligible gold bars must meet the same purity standards and must be manufactured by COMEX-traded firms.
- No scrap gold, jewelry box gold, or junk gold is allowed in an IRA.
Where Gold Is Stored?
Owning gold in an IRA is one of the safest ways to own physical gold. We’ve covered the quality and purity benchmarks, and the standards for storage are just as exacting.
Because you cannot take physical possession of the assets in your IRA without taking a distribution, the physical gold must be stored in a neutral, guarded, and insured location. These locations are called depositories. A depository is a large vault.
The IRS has a long list of stringent guidelines that must be met before it approves a depository as a safe place to store precious metals. Vault size, security, service area, management, and record-keeping must meet strict standards. Only the best of the best receive the seal of approval and can accept metals on your behalf.
Once metals arrive at the depository, one of the institution’s important tasks is to thoroughly inspect them to ensure they are what they are supposed to be. It must also make sure the metals meet the requirements for IRA investments.
The depository inspects, weighs, photographs, and authenticates the gold before accepting it and placing it into the vault in your gold IRA custodian’s designated section for safekeeping.
The depositories are insured and have elaborate measures to help prevent loss or damage.
Some of the most preferred depositories for Gold IRA storage include:
- The Delaware Depository
- Brinks Depository
- JPMorgan
- HSBC Bank
How To Withdraw From A Gold IRA
It’s your money in your IRA, and you are entitled to it at any time. However, it is important to understand the rules for taking a distribution to prevent triggering a taxable event or even incurring a penalty.
Whether your account is a traditional, a Roth, or a SEP, you can withdraw funds with no penalty after the age of 59½. Traditional and SEP withdrawals at that age and beyond are considered ordinary income and are taxed as such. Roth withdrawals are not subject to taxation, as funds are deposited into a Roth after taxes are paid.
At age 73, SEP and traditional IRA owners must begin to draw down on their accounts and take required minimum distributions. RMDs are the government’s way of making sure you start paying the deferred taxes on the money in your IRA.
Roth owners are not subject to RMDs.
Physical gold owners may take their distributions “in kind,” meaning they can opt to have their physical gold sent to them from the depository as their distribution. This allows you to keep owning the gold you’ve acquired, which can continue to work for you.
Open A Gold IRA
Ready to open your Gold IRA? The next step is to get you started, and that’s where the experts at Advantage Gold come in. Contact us, and we will be happy to help you get started and show you how a Gold IRA works to meet your needs.
Tags: how do gold iras work


